Imagine a smart contract that promises to pay you $100 if the price of Bitcoin hits $60,000. Sounds simple, right? But here’s the problem: blockchains don’t know what’s happening outside their own network. They can’t check the price of Bitcoin on Coinbase, Binance, or any live market. That’s where Chainlink comes in. It’s the bridge between blockchain smart contracts and the real world - and without it, most DeFi apps wouldn’t work at all.
What Is a Blockchain Oracle?
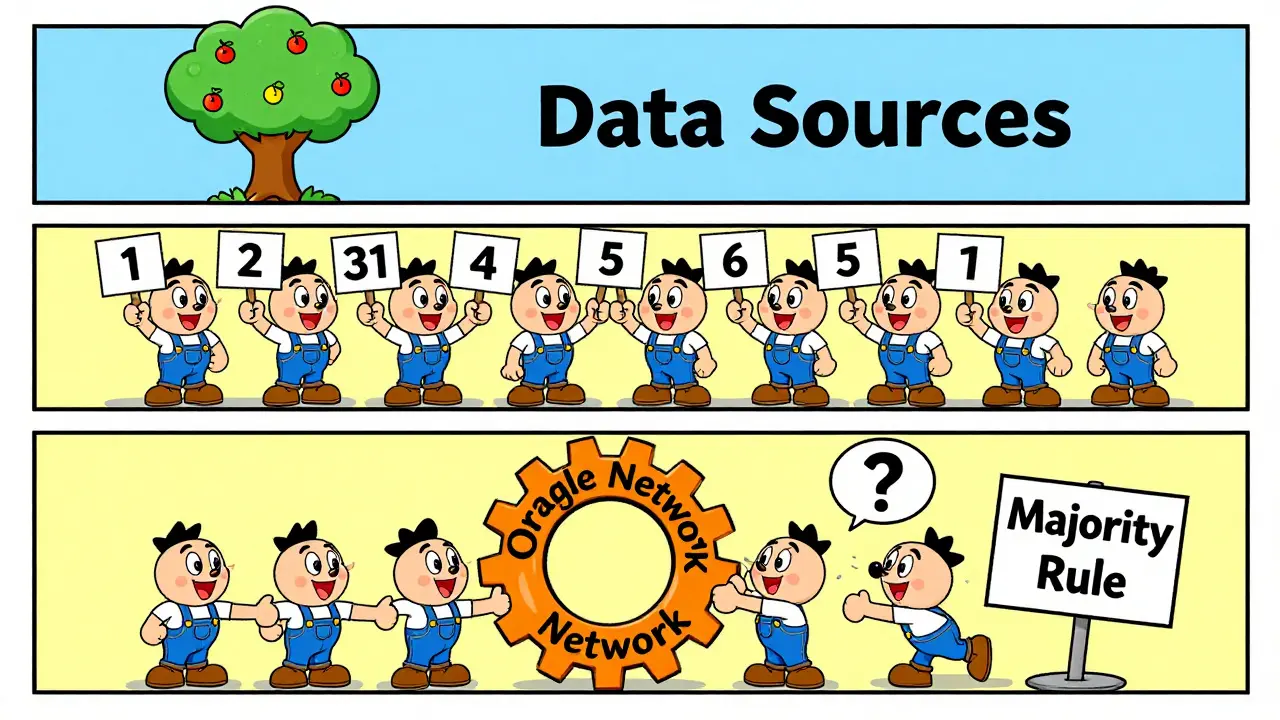
A blockchain oracle is essentially a data feed. Smart contracts can’t pull information from websites, APIs, or sensors on their own. They’re isolated systems. So if you want a contract to react to stock prices, weather data, or sports scores, you need something to bring that info in. That’s an oracle. Early oracles were centralized - one company, one server, one API. If that server went down or got hacked, the whole contract failed. That’s a huge risk when millions of dollars are on the line. Chainlink solved this by making the oracle itself decentralized. Instead of one source, it uses dozens, sometimes hundreds, of independent data providers. Each one fetches the same data, and the system only accepts the result if most of them agree. No single point of failure. No single company in control.How Chainlink Works: The Three Layers of Decentralization
Chainlink doesn’t just use many data sources - it layers its security. Here’s how it works:- Data Source Level: Chainlink pulls data from multiple APIs - CoinGecko, Tiingo, Alpha Vantage, and more. If one API gives bad data, others can override it.
- Node Operator Level: Thousands of independent operators run Chainlink nodes. These aren’t controlled by Chainlink Inc. They’re volunteers, companies, or developers who set up servers to fetch and verify data. They get paid in LINK tokens for honest work.
- Oracle Network Level: Multiple node operators form a network for each data request. They don’t just report data - they validate each other. If 8 out of 10 nodes say Bitcoin is at $59,800, the contract accepts that. One outlier? Ignored.
This three-layer approach makes Chainlink the most secure oracle network in existence. Even if one layer fails, the others hold.
The LINK Token: Incentivizing Honest Behavior
LINK isn’t a currency you trade like Bitcoin. It’s a utility token that keeps the network running. Node operators must stake LINK to participate. When they deliver accurate data, they earn more LINK. If they lie, cheat, or go offline, they lose LINK. It’s a simple economic model: good behavior gets rewarded, bad behavior gets punished.LINK uses the ERC-677 standard - an upgrade from ERC-20 that lets data be sent along with token transfers. This means a smart contract can request data and pay for it in one transaction. No need for separate payments. No middlemen.
Chainlink Price Feeds: The Backbone of DeFi
The most widely used Chainlink service is Price Feeds. These are pre-built, constantly updating data streams for crypto prices, forex rates, and commodity values. They’re used by Aave, Compound, Synthetix, and dozens of other major DeFi protocols.As of 2023, Chainlink Price Feeds secure over $30 billion in DeFi assets. They update every 60 minutes under normal conditions, but during market swings - like when Elon Musk tweets - they refresh in seconds. And every update comes with a cryptographic proof that the data hasn’t been tampered with. No guesswork. No trust. Just math.
Chainlink 2.0: The Next Evolution
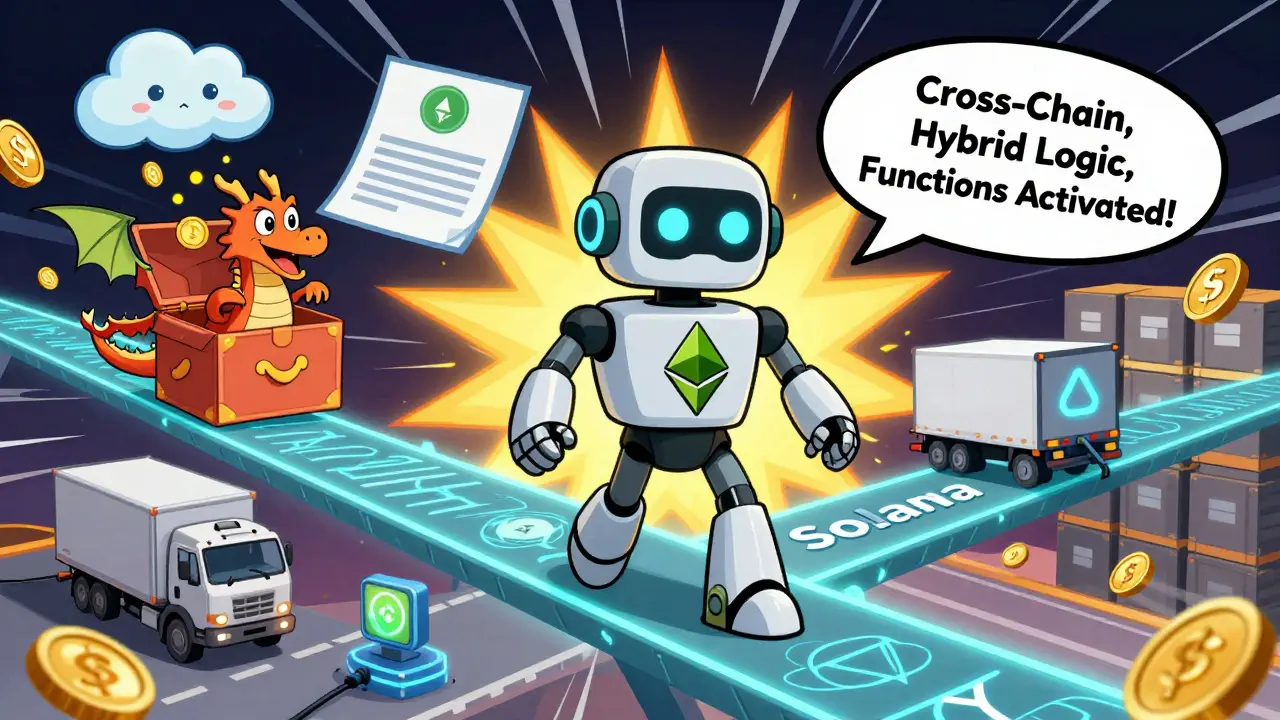
Chainlink didn’t stop at Price Feeds. In 2023, it launched Chainlink 2.0 - a major upgrade that adds:- Hybrid Smart Contracts: Contracts that can run complex logic off-chain (like AI analysis or big data processing) while still being secured on-chain.
- Chainlink Functions: Lets smart contracts directly call any public API without needing a custom oracle. Just write a simple JavaScript function, and Chainlink runs it securely off-chain.
- Staking v0.2: Improved economics for node operators - better rewards, fewer penalties for minor downtime.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP): Lets smart contracts on Ethereum talk to those on Solana, Polygon, or any other chain. No more siloed ecosystems.
These upgrades aren’t just features - they’re building blocks for the next generation of blockchain applications. Imagine a loan contract that checks your credit score from Equifax, verifies your employment via ADP, and then disburses funds based on real-time market conditions - all automatically. That’s what Chainlink 2.0 enables.
Real-World Use Cases Beyond DeFi
Chainlink isn’t just for crypto traders. It’s being used in:- Asset Tokenization: Companies like BlackRock and Siemens use Chainlink’s Proof of Reserve (PoR) to prove that tokenized real-world assets (like gold or real estate) are fully backed. No fraud. No guesswork.
- Insurance: Parametric insurance contracts pay out automatically when weather data from NOAA confirms a hurricane hit a specific area.
- Gaming: Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function) generates provably fair random numbers for NFT drops and loot boxes. No one can rig the outcome.
- Supply Chain: Smart contracts trigger payments when IoT sensors confirm a shipment reached its destination.
Over 1,000 projects across 10+ blockchains use Chainlink. It’s not a niche tool - it’s infrastructure.
How Developers Use Chainlink
To integrate Chainlink into a smart contract, you need three things:- A consumer contract: Your own smart contract that asks for data. Written in Solidity.
- A Chainlink job specification: Tells the oracle what data to fetch and where from.
- LINK tokens: To pay for the data request. You must fund your contract with LINK.
It’s not plug-and-play. Developers report a steep learning curve. Setting up a custom oracle can take weeks if you’re new. But Chainlink’s documentation is extensive - over 200 code examples and 50+ video tutorials. Reddit and GitHub are full of success stories. One developer on GitHub said they went 18 months without a single failed request.
Most beginners start with Chainlink Price Feeds. They’re pre-built, reliable, and well-documented. You don’t need to run a node. You just call the feed, pay a little LINK, and get live prices.
Competition and Criticism
Chainlink isn’t the only oracle. Band Protocol, API3, and Tellor offer alternatives. But none match its scale or security.API3, for example, lets data providers (like Bloomberg or CoinMarketCap) run their own nodes. It’s more direct - but less decentralized. If Bloomberg’s node goes down, your contract fails. Chainlink doesn’t rely on any single provider.
Critics point to one issue: cost. Node operators need to be paid, and LINK token prices fluctuate. During bear markets, some operators drop off because rewards don’t cover costs. Chainlink 2.0’s improved staking and incentive structures aim to fix this. Early signs are positive - node operator participation has grown 40% since Q1 2023.
Another concern? Complexity. Writing a consumer contract isn’t easy. But that’s the price of security. If you want your contract to handle millions in assets, you need a system that’s bulletproof - not simple.
What’s Next for Chainlink?
In 2024, Chainlink is pushing into enterprise finance. DTCC - the giant clearinghouse for U.S. stock trades - is piloting Chainlink for tokenized securities settlement. That’s not a small experiment. It’s the traditional financial world adopting blockchain infrastructure.Gartner predicts that by 2026, 80% of enterprise blockchain apps will need oracle solutions. Chainlink is already there. With CCIP, Functions, and growing institutional adoption, it’s not just leading the market - it’s defining it.
Chainlink doesn’t just connect blockchains to the real world. It’s making the real world run on blockchains.
What is the main purpose of the Chainlink oracle network?
The main purpose of the Chainlink oracle network is to securely connect smart contracts on blockchains to real-world data - like cryptocurrency prices, stock markets, weather, or sports results. Without oracles, smart contracts can’t access external information, which limits their usefulness. Chainlink solves this by using a decentralized network of node operators to fetch, verify, and deliver accurate data, ensuring contracts execute correctly based on real events.
How does Chainlink ensure data accuracy?
Chainlink ensures data accuracy through a multi-layered approach. It pulls data from multiple independent sources (like CoinGecko, Tiingo, and Alpha Vantage), then aggregates results from dozens of decentralized node operators. Only if a majority of nodes agree on the data does the smart contract accept it. Each data point comes with a cryptographic proof, making tampering impossible. This system removes reliance on any single source or operator.
What role does the LINK token play in the Chainlink network?
The LINK token is the native currency of the Chainlink network. Node operators must be paid in LINK to fulfill data requests. They earn LINK for delivering accurate, timely data and lose LINK if they provide false or delayed information. This economic incentive structure encourages honest behavior. Users also need LINK to pay for data services - for example, when a smart contract requests a Bitcoin price feed.
What’s the difference between Chainlink 1.0 and Chainlink 2.0?
Chainlink 1.0 focused on basic oracle services like Price Feeds and VRF. Chainlink 2.0 expands this with new capabilities: hybrid smart contracts that run complex off-chain logic, Chainlink Functions for direct API calls without custom code, Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) for communication between blockchains, and improved staking economics for node operators. In short, 2.0 turns Chainlink from a data feed into a full decentralized infrastructure layer.
Can I use Chainlink without running a node?
Yes, absolutely. Most users don’t run nodes. Developers integrate Chainlink services like Price Feeds or VRF directly into their smart contracts using pre-built templates. All you need is a small amount of LINK to pay for data requests. Running a node is only necessary if you want to earn LINK by providing data - which requires technical setup, hardware, and staking capital.
Is Chainlink the only oracle network available?
No, there are alternatives like Band Protocol, API3, and Tellor. But Chainlink is the most widely adopted, securing over $30 billion in DeFi assets and used by more than 1,000 projects. Its multi-layered decentralization, extensive documentation, and enterprise partnerships give it a significant edge. While alternatives may be simpler or cheaper, none match Chainlink’s security, scale, or ecosystem support.
